Plastic deformation refers to the process in which a structure experiences external stress beyond its yield limit, transitioning from elastic deformation to plastic deformation. This process is also referred to as elastoplastic deformation. Plastic deformation is commonly seen in industrial applications, such as the formation of various sheet metal and die casting of automobile bodies. In a professional engineering context, engineers aim to avoid plastic deformation in structures to prevent material failure. As a result, plastic analysis is very common in structural finite element analysis.

The general-purpose engineering simulation software WELSIM already supports plastic analysis. This article gives an overview of the plastic analysis features in the current version from a practical software usage perspective.
From a computational standpoint, plastic deformation is a nonlinear process in a material’s constitutive relationship. Therefore, the software must have the capabilities to solve nonlinear problems. WELSIM uses FrontISTR as its implicit solver and OpenRadioss as its explicit solver. Users can also use other solvers such as CalculiX and Elmer, which will be covered in future articles. This article focuses on the FrontISTR and OpenRadioss solvers.
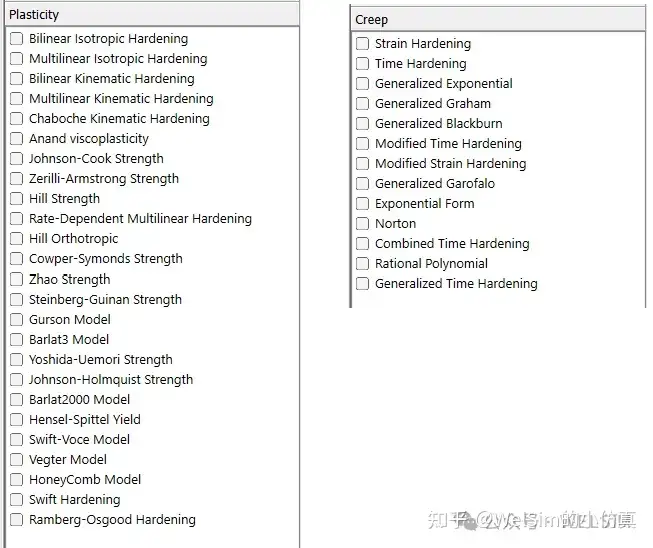
Most of the complexity in plastic deformation lies in the material behavior. Therefore, considerable effort is required for the material data input and editing. With the diversity of plastic models, the front-end interface also needs to be robust. WELSIM provides a user-friendly material editor and a fully consistent, free standalone material software called MatEditor. Currently, 25 plastic-related and 12 creep-related material properties are supported. Each property has its own parameters and editing method.

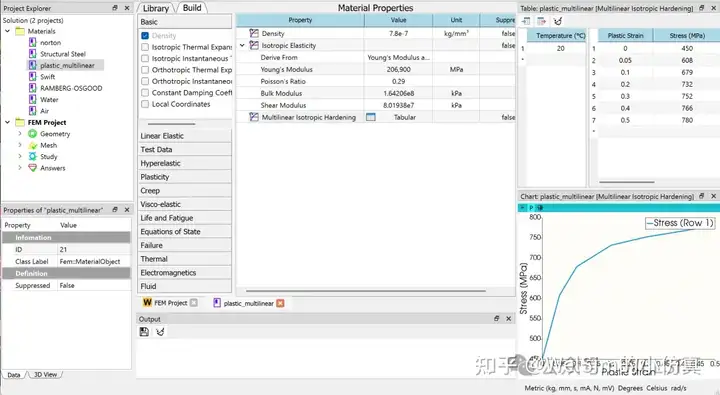
Using multilinear hardening as an example, the figure below demonstrates how to define an elastoplastic material. Basic parameters are entered:
- Density:
7.8e-7 kg/mm³ - Young’s modulus:
206.9 GPa - Poisson’s ratio:
0.29
Plastic stress-strain relationship data:
- Strain:
{0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5} - Stress:
{450, 608, 679, 732, 752, 766, 780} MPa

Static elastoplastic analysis
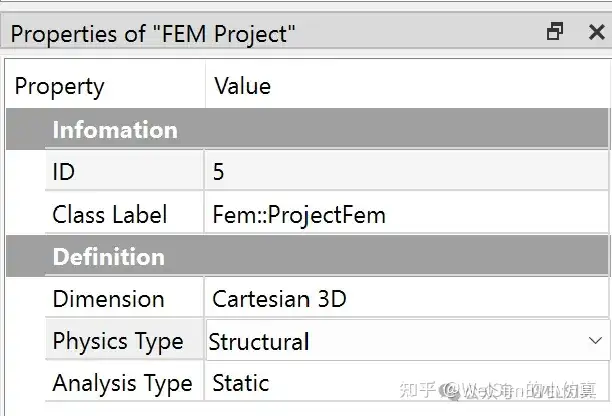
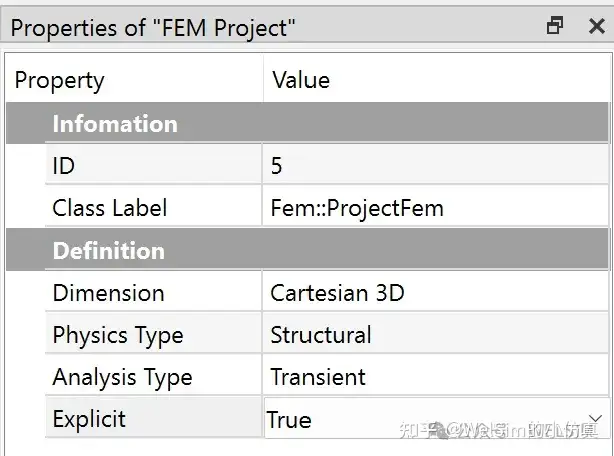
For static nonlinear finite element analysis, the computation is essentially implicit. Nonlinear material deformation is solved using the Newton iterative method. In the project settings, you can retain the default “Static Structural Analysis” type.

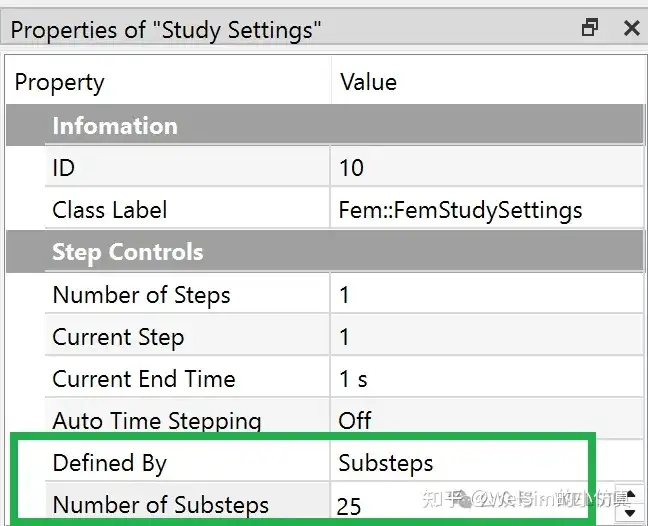
Because plastic deformation is a nonlinear process, multiple sub-steps can be set in the analysis. In this example, 25 sub-steps are used.

The other analysis settings are almost identical to those in elastic analysis.
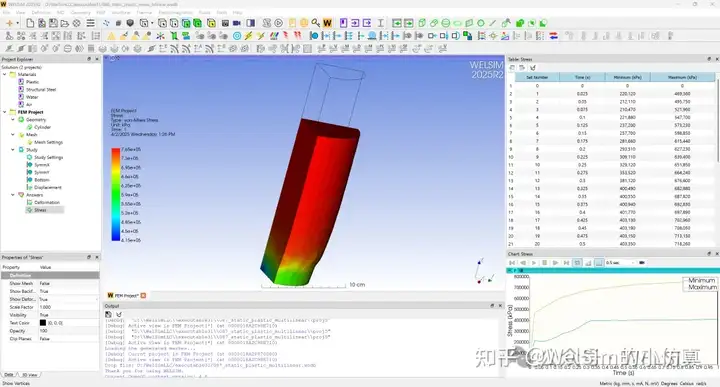
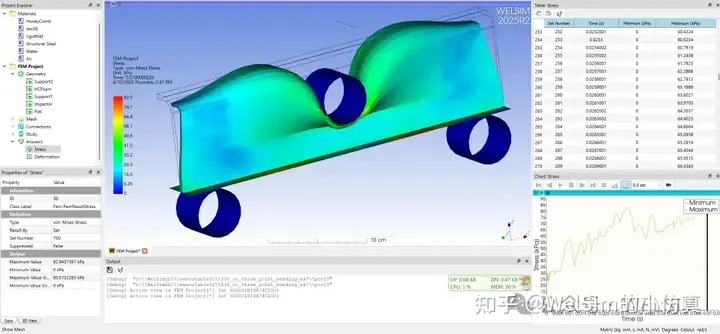
After setting boundary conditions and running the simulation, you will obtain common results like stress and displacement. For simple models, the stress results can also reflect the plasticity.

WELSIM uses FrontISTR as the default solver for static structural analysis. Supported default plastic models include:
- Bilinear
- Multilinear
- Swift
- Ramberg-Osgood
- Kinematic Hardening
Transient elastoplastic analysis
For WELSIM’s transient structural analysis, it is recommended to use explicit method with OpenRadioss as the solver. OpenRadioss is an excellent open source solver for structural dynamics, known for reliable results, and it supports a wide variety of plastic models.
In the project settings, set the analysis type to “Transient” and enable “Explicit” analysis.

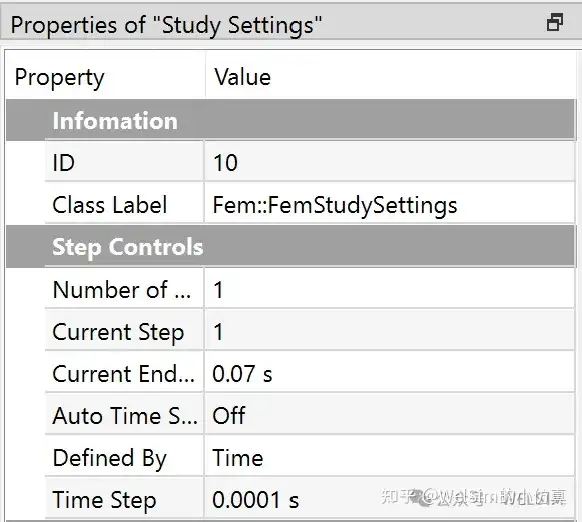
In transient analysis, it’s often necessary to set the physical time for each load step and time step. As shown in the figure:
- Total time:
0.07s - Time step:
0.0001s

After defining boundary conditions and running the computation, results can be obtained.

Supported plastic models for explicit transient analysis are given below:
- LAW2 (PLAS_JOHNS) — Density + Isotropic Elasticity + Johnson-Cook
- PLAS_ZERIL — Density + Isotropic Elasticity + Zerilli-Armstrong
- LAW22 (DAMA) — Density + Isotropic Elasticity + Johnson-Cook + General Damage
- LAW27 (PLAS_BRIT) — Density + Isotropic Elasticity + Johnson-Cook + Orthotropic Brittle Failure
- LAW28 (HONEYCOMB) — Density + Honeycomb
- LAW32 (HILL) — Hill
- LAW36 (PLAS_TAB) — Density + Isotropic Elasticity + Rate-Dependent Multilinear Hardening
- LAW44 (COWPER) — Cowper-Symonds
- LAW93 (ORTH_HILL) — Orthotropic Hill
- LAW48 (ZHAO) — Zhao
- LAW49 (STEINB) — Steinberg-Guinan
- LAW52 (GURSON) — Gurson
- LAW57 (BARLET3) — Barlet3
- LAW78 — Yoshida-Uemori
- LAW79 (JOHN_HOLM) — Johnson-Holmquist
- LAW84 — Swift-Voce
- LAW103 (HENSEL-SPITTEL) — Hensel-Spittel
- LAW110 (VEGTER) — Vegter
Note: WELSIM does not include OpenRadioss in its installation package. Users need to download OpenRadioss separately and configure its directory in WELSIM’s preferences before using it for the first time.
Conclusion
This article introduces how to use WELSIM to perform finite element analysis (FEA) on structures with plastic materials. With its excellent material editing module and powerful solvers like OpenRadioss and FrontISTR, users can carry out plastic structural analysis and obtain results quickly.
WelSim and author are not directly related to the OpenRadioss, FrontISTR, Elmer, or CalculiX development team. The reference to OpenRadioss FrontISTR, Elmer, or CalculiX is only used here for technical blog and software usage references.